EllipseDeep Learning in C
A lightweight, high-performance numerical computing library for deep learning written in pure C. Inspired by PyTorch, micrograd, and XLA.

Why Ellipse?
Built for performance, designed for simplicity
Lightweight Design
Focused on simplicity, providing core deep learning operations without heavy dependencies. Perfect for embedded systems and resource-constrained environments.
Pure C Implementation
Built entirely in C for maximum portability and optimized low-level manipulation. No external dependencies, runs anywhere C runs.
Advanced Features
Includes automatic differentiation, flexible tensor operations, lazy backpropagation, and a modular architecture for easy extension.
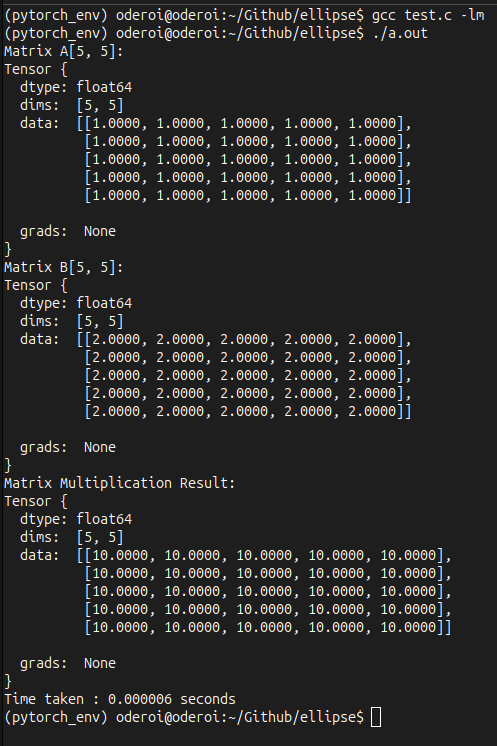
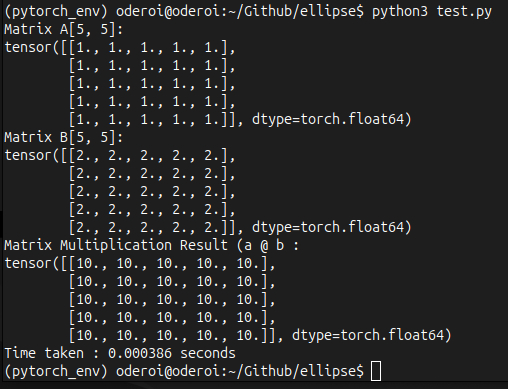
Performance Comparison
Real-world benchmarks comparing Ellipse and PyTorch
Execution Time
Memory Usage
Binary Size
CPU Efficiency

Ellipse
Lightweight & Fast
PyTorch
Industry Standard
Key Takeaways
Ellipse delivers comparable performance with significantly lower resource requirements
Who is This For?
Perfect for developers who want to understand and control every aspect of deep learning
Learning & Education
Understand deep learning libraries from the ground up with clean, readable C code
Resource-Limited
Run neural networks in embedded systems, IoT devices, and low-resource environments
Custom ML Operations
Prototype and implement custom ML operations in C with full control over the stack
Ready to Get Started?
Ellipse is open source and welcomes contributions from the community. Join us in building the future of lightweight deep learning.